13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(6):2367-2378. doi:10.7150/thno.94788 This issue Cite
Review
Theranostics and artificial intelligence: new frontiers in personalized medicine
1. Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA.
2. Department of Oncology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA.
3. Department of Immunology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA.
4. Department of Urology, Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN, USA.
Abstract
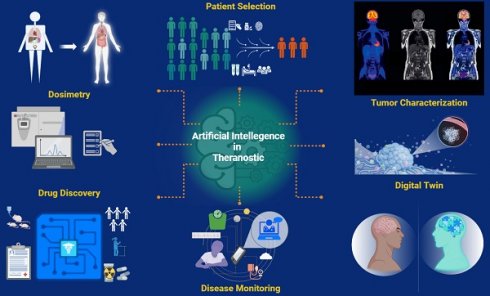
The field of theranostics is rapidly advancing, driven by the goals of enhancing patient care. Recent breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI) and its innovative theranostic applications have marked a critical step forward in nuclear medicine, leading to a significant paradigm shift in precision oncology. For instance, AI-assisted tumor characterization, including automated image interpretation, tumor segmentation, feature identification, and prediction of high-risk lesions, improves diagnostic processes, offering a precise and detailed evaluation. With a comprehensive assessment tailored to an individual's unique clinical profile, AI algorithms promise to enhance patient risk classification, thereby benefiting the alignment of patient needs with the most appropriate treatment plans. By uncovering potential factors unseeable to the human eye, such as intrinsic variations in tumor radiosensitivity or molecular profile, AI software has the potential to revolutionize the prediction of response heterogeneity. For accurate and efficient dosimetry calculations, AI technology offers significant advantages by providing customized phantoms and streamlining complex mathematical algorithms, making personalized dosimetry feasible and accessible in busy clinical settings. AI tools have the potential to be leveraged to predict and mitigate treatment-related adverse events, allowing early interventions. Additionally, generative AI can be utilized to find new targets for developing novel radiopharmaceuticals and facilitate drug discovery. However, while there is immense potential and notable interest in the role of AI in theranostics, these technologies do not lack limitations and challenges. There remains still much to be explored and understood. In this study, we investigate the current applications of AI in theranostics and seek to broaden the horizons for future research and innovation.
Keywords: artificial intelligence, machine learning, theranostics, tumor dosimetry, drug discovery, nuclear medicine
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact