13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2013; 3(2):99-108. doi:10.7150/thno.5361 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Synthesis of Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS Core/Shell Quantum Dots with Inhibited Blue-Shift Photoluminescence and Applications for Tumor Targeted Bioimaging
1. Institute of Nanobiotechnology, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tianjin University and Tianjin Key Laboratory of Composites and Functional Materials, Tianjin, 300072, China.
2. Department of Medical Radioprotection, School of Radiation Medicine and Health, Soochow University, Suzhou, 200072, China.
3. The Institute for Biomedical Engineering & Nano Science, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200092, China.
4. Imaging Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, Jiangsu Province, 215006, China.
Abstract
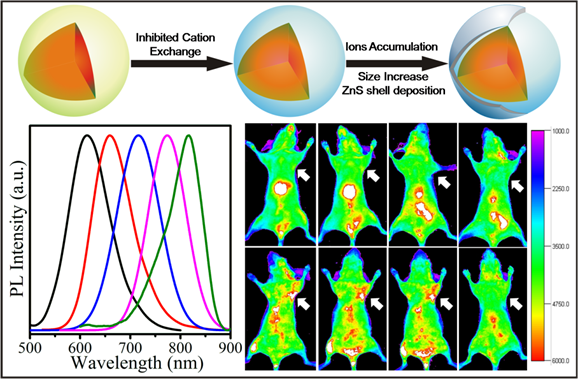
A facile strategy is reported here for synthesis of Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS (ZCIS/ZnS) core/shell QDs to address the synthetic issues that the unexpected blue-shift of CuInS2-based nanocrystals. In this strategy, Zn2+ ions are intentionally employed for the synthesis of alloyed ZCIS core QDs before ZnS shell coating, which contributes to the reduced blue-shift in photoluminescence (PL) emission. The experimental results demonstrate this elaborate facile strategy is effective for the reduction of blue-shift during shell growth. Particularly, a hypothesis is proposed and proved for explanation of this effective strategy. Namely, both cation exchange inhibition and ions accumulation are involved during the synthesis of ZCIS/ZnS QDs. Furthermore, the obtained near infrared (NIR) ZCIS/ZnS QDs are transferred into aqueous phase by a polymer coating technique and coupled with cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp peptide (cRGD) peptides. After confirmation of biocompability by cytotoxicity test on normal 3T3 cells, these QDs are injected via tail vein into nude mice bearing U87 MG tumor. The result indicates that the signals detected in the tumor region are much more distinguishing injected with ZCIS/ZnS-cRGD QDs than that injected with ZCIS/ZnS QDs.
Keywords: CuInS2, Near-infrared, In vivo imaging, Blue shift, Tumor Targeting.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact