13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(14):7005-7017. doi:10.7150/thno.57404 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Nanoparticle encapsulation of non-genotoxic p53 activator Inauhzin-C for improved therapeutic efficacy
1. Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology and Cancer Center, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA.
2. Department of Chemistry, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA, USA.
3. Laboratory of Cellular Immunology, Ochsner Clinic Foundation, New Orleans, LA 70121, USA.
4. Department of Chemistry, Tulane University School of Science and Engineering, New Orleans, LA, USA.
5. Department of Pathology, Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans, LA, USA.
Abstract
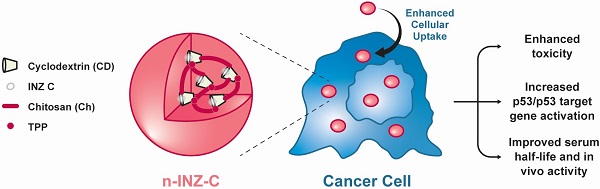
The tumor suppressor protein p53 remains in a wild type but inactive form in ~50% of all human cancers. Thus, activating it becomes an attractive approach for targeted cancer therapies. In this regard, our lab has previously discovered a small molecule, Inauhzin (INZ), as a potent p53 activator with no genotoxicity.
Method: To improve its efficacy and bioavailability, here we employed nanoparticle encapsulation, making INZ-C, an analog of INZ, to nanoparticle-encapsulated INZ-C (n-INZ-C).
Results: This approach significantly improved p53 activation and inhibition of lung and colorectal cancer cell growth by n-INZ-C in vitro and in vivo while it displayed a minimal effect on normal human Wi38 and mouse MEF cells. The improved activity was further corroborated with the enhanced cellular uptake observed in cancer cells and minimal cellular uptake observed in normal cells. In vivo pharmacokinetic evaluation of these nanoparticles showed that the nanoparticle encapsulation prolongates the half-life of INZ-C from 2.5 h to 5 h in mice.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate that we have established a nanoparticle system that could enhance the bioavailability and efficacy of INZ-C as a potential anti-cancer therapeutic.
Keywords: p53, nanoparticle encapsulation, Inauhzin-C, PK, cell growth, efficacy, anti-cancer therapy, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact