13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(16):7685-7699. doi:10.7150/thno.60190 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Attenuation of tonic inhibition prevents chronic neurovascular impairments in a Thy1-ChR2 mouse model of repeated, mild traumatic brain injury
1. University of Toronto, Department of Medical Biophysics, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
2. Physical Sciences, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
3. Biological Sciences, Sunnybrook Research Institute, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
4. Mouse Imaging Centre, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
5. Neuropsychiatry Program, Department of Psychiatry and Division of Neurology, Department of Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada.
6. Division of Cognitive Neurology, Department of Neurology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
7. University of Toronto, Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Abstract
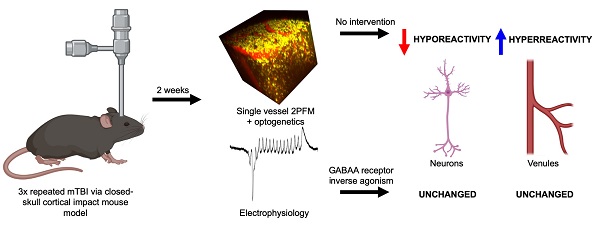
Rationale: Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), the most common type of brain trauma, frequently leads to chronic cognitive and neurobehavioral deficits. Intervening effectively is impeded by our poor understanding of its pathophysiological sequelae.
Methods: To elucidate the long-term neurovascular sequelae of mTBI, we combined optogenetics, two-photon fluorescence microscopy, and intracortical electrophysiological recordings in mice to selectively stimulate peri-contusional neurons weeks following repeated closed-head injury and probe individual vessel's function and local neuronal reactivity.
Results: Compared to sham-operated animals, mTBI mice showed doubled cortical venular speeds (115 ± 25%) and strongly elevated cortical venular reactivity (53 ± 17%). Concomitantly, the pericontusional neurons exhibited attenuated spontaneous activity (-57 ± 79%) and decreased reactivity (-47 ± 28%). Post-mortem immunofluorescence revealed signs of peri-contusional senescence and DNA damage, in the absence of neuronal loss or gliosis. Alteration of neuronal and vascular functioning was largely prevented by chronic, low dose, systemic administration of a GABA-A receptor inverse agonist (L-655,708), commencing 3 days following the third impact.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that repeated mTBI leads to dramatic changes in the neurovascular unit function and that attenuation of tonic inhibition can prevent these alterations. The sustained disruption of the neurovascular function may underlie the concussed brain's long-term susceptibility to injury, and calls for development of better functional assays as well as of neurovascularly targeted interventions.
Keywords: Traumatic brain injury, Two-photon fluorescence microscopy, Optogenetics, Neurovascular coupling, L-655, 708
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact