13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(13):5824-5835. doi:10.7150/thno.75200 This issue Cite
Research Paper
LRRC8A critically regulates myofibroblast phenotypes and fibrotic remodeling following myocardial infarction
1. Department of Geriatrics, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, 710032 China.
2. Department of Cardiology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, 710032 China.
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
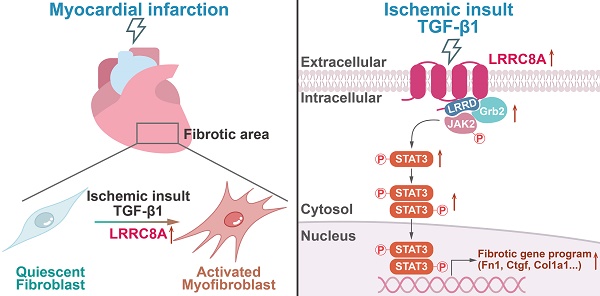
Rationale: The transformation of fibroblasts into activated myofibroblasts is a critical step that results in cardiac fibrosis upon myocardial infarction (MI). Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein-8A (LRRC8A) is a multi-functional protein involved in cell survival, growth, and proliferation, whereas its role in regulating myofibroblast phenotypes and myocardial fibrosis remains unknown.
Methods: Conditional myofibroblast-specific Lrrc8a knockout mouse models were established by crossing the Lrrc8aflox/flox mice with the tamoxifen-inducible periostin-Cre transgenic mice. The involvement of LRRC8A in regulating cardiac fibrosis post-MI and myofibroblast phenotypes induced by transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) was comprehensively evaluated. The mechanisms underlying LRRC8A regulation of myofibroblast phenotypes were determined by RNA sequencing-driven analysis followed by cause-effect experiments.
Results: LRRC8A expression was significantly elevated in the fibrotic tissues and the fibroblasts isolated from the post-MI hearts. Compared with the wild-type (WT) littermates, the specific knockout of LRRC8A in myofibroblasts greatly attenuated myofibroblast transformation, fibrotic remodeling, and ventricular dysfunction after MI. Silencing of LRRC8A expression suppressed, whereas overexpression of LRRC8A enhanced, the pro-fibrotic myofibroblast phenotypes in isolated cardiac fibroblasts upon stimulation with TGF-β1. LRRC8A participated in TGF-β1-induced myofibroblast transformation via activating JAK2-STAT3 signaling. Furthermore, LRRC8A activated the JAK2-STAT3 pathway via its C-terminal leucine-rich repeat-domain (LRRD), directly interacting with growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 (GRB2), an adaptor protein associated with and necessary for tyrosine-phosphorylated JAK2.
Conclusions: LRRC8A regulates myofibroblast transformation and cardiac fibrosis following MI. LRRC8A inhibition might be a promising strategy for cardiac fibrosis and heart failure.
Keywords: fibrosis, heart failure, leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 8A, myocardial infarction, myofibroblast.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact