13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(2):460-479. doi:10.7150/thno.87329 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Differential effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles on cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-876-3p
1. Department of Microbiology and Immunology, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-412, Korea.
2. Department of Oral Pathology, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-412, Korea.
3. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 700-412, Korea.
Abstract
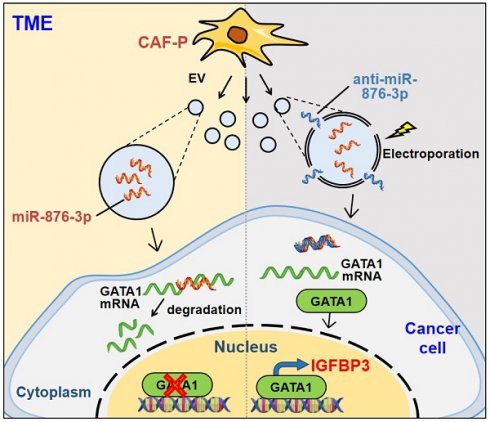
Rationale: Platinum-based chemotherapy is commonly used for treating solid tumors, but drug resistance often limits its effectiveness. Cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-derived extracellular vesicle (EV), which carry various miRNAs, have been implicated in chemotherapy resistance. However, the molecular mechanism through which CAFs modulate cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is not well understood. We employed two distinct primary CAF types with differential impacts on cancer progression: CAF-P, representing a more aggressive cancer-promoting category, and CAF-D, characterized by properties that moderately delay cancer progression. Consequently, we sought to investigate whether the two CAF types differentially affect cisplatin sensitivity and the underlying molecular mechanism.
Methods: The secretion profile was examined by utilizing an antibody microarray with conditioned medium obtained from the co-culture of OSCC cells and two types of primary CAFs. The effect of CAF-dependent factors on cisplatin resistance was investigated by utilizing conditioned media (CM) and extracellular vesicle (EVs) derived from CAFs. The impacts of candidate genes were confirmed using gain- and loss-of-function analyses in spheroids and organoids, and a mouse xenograft. Lastly, we compared the expression pattern of the candidate genes in tissues from OSCC patients exhibiting different responses to cisplatin.
Results: When OSCC cells were cultured with conditioned media (CM) from the two different CAF groups, cisplatin resistance increased only under CAF-P CM. OSCC cells specifically expressed insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) after co-culture with CAF-D. Meanwhile, IGFBP3-knockdown OSCC cells acquired cisplatin resistance in CAF-D CM. IGFBP3 expression was promoted by GATA-binding protein 1 (GATA1), a transcription factor targeted by miR-876-3p, which was enriched only in CAF-P-derived EV. Treatment with CAF-P EV carrying miR-876-3p antagomir decreased cisplatin resistance compared to control miRNA-carrying CAF-P EV. On comparing the staining intensity between cisplatin-sensitive and -insensitive tissues from OSCC patients, there was a positive correlation between IGFBP3 and GATA1 expression and cisplatin sensitivity in OSCC tissues from patients.
Conclusion: These results provide insights for overcoming cisplatin resistance, especially concerning EVs within the tumor microenvironment. Furthermore, it is anticipated that the expression levels of GATA1 and miR-876-3p, along with IGFBP3, could aid in the prediction of cisplatin resistance.
Keywords: cisplatin resistance, cancer-associated fibroblasts, extracellular vesicles, insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3, hsa-miR-876-3p
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact