13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(7):2934-2945. doi:10.7150/thno.95267 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A non-lipid nucleic acid delivery vector with dendritic cell tropism and stimulation
1. Center for Systems Biology, Massachusetts General Hospital, 185 Cambridge St, CPZN 5206, Boston, MA 02114, USA.
2. Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, 200 Longwood Ave, Boston, MA 02115, USA.
3. Harvard Master's Program in Immunology, Harvard Medical School, 200 Longwood Ave, Boston, MA 02114, USA.
* Equal contribution.
Abstract
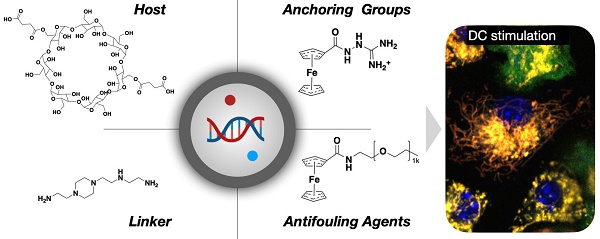
Rationale: Nucleic acid constructs are commonly used for vaccination, immune stimulation, and gene therapy, but their use in cancer still remains limited. One of the reasons is that systemic delivery to tumor-associated antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells and macrophages) is often inefficient, while off-target nucleic acid-sensing immune pathways can stimulate systemic immune responses. Conversely, certain carbohydrate nanoparticles with small molecule payloads have been shown to target these cells efficiently in the tumor microenvironment. Yet, nucleic acid incorporation into such carbohydrate-based nanoparticles has proven challenging.
Methods: We developed a novel approach using cross-linked bis succinyl-cyclodextrin (b-s-CD) nanoparticles to efficiently deliver nucleic acids and small-molecule immune enhancer to phagocytic cells in tumor environments and lymph nodes. Our study involved incorporating these components into the nanoparticles and assessing their efficacy in activating antigen-presenting cells.
Results: The multi-modality immune stimulators effectively activated antigen-presenting cells and promoted anti-tumor immunity in vivo. This was evidenced by enhanced delivery to phagocytic cells and subsequent immune response activation in tumor environments and lymph nodes.
Conclusion: Here, we describe a new approach to incorporating both nucleic acids and small-molecule immune enhancers into cross-linked bis succinyl-cyclodextrin (b-s-CD) nanoparticles for efficient delivery to phagocytic cells in tumor environments and lymph nodes in vivo. These multi-modality immune stimulators can activate antigen-presenting cells and foster anti-tumor immunity. We argue that this strategy can potentially be used to enhance anti-tumor efficacy.
Keywords: nucleic acid delivery, nanoparticles, dendritic cells, vaccine, cancer, lymph node
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact