13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(19):7292-7308. doi:10.7150/thno.99323 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Circular RNA SCMH1 suppresses KMO expression to inhibit mitophagy and promote functional recovery following stroke
1. Jiangsu Provincial Key Laboratory of Critical Care Medicine, Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, China.
2. Co-innovation Center of Neuroregeneration, Nantong University, Nantong, China.
3. Institute of Life Sciences, Key Laboratory of Developmental Genes and Human Disease, Southeast University, Nanjing, China.
Abstract
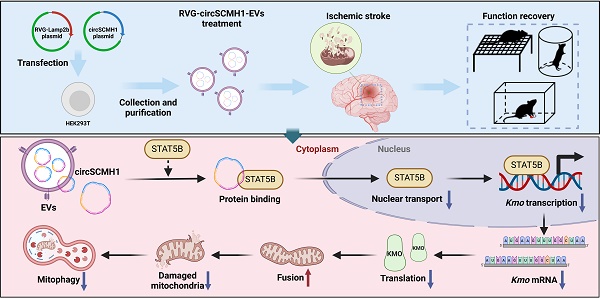
Rationale: Metabolic dysfunction is one of the key pathological events after ischemic stroke. Disruption of cerebral blood flow impairs oxygen and energy substrate delivery, leading to mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation dysfunction and cellular bioenergetic stress. Investigating the effects of circSCMH1, a brain repair-related circular RNA, on metabolism may identify novel therapeutic targets for stroke treatment.
Methods: CircSCMH1 was encapsulated into brain-targeting extracellular vesicles (EVs) mediated by rabies virus glycoprotein (RVG). Using a mouse model of photothrombotic (PT) stroke, we employed metabolomics and transcriptomics, combined with western blotting and behavioral experiments, to identify the metabolic targets regulated in RVG-circSCMH1-EV-treated mice. Additionally, immunofluorescence staining, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), pull-down, and western blotting were utilized to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Results: The targeted delivery of circSCMH1 via RVG-EVs was found to promote post-stroke brain repair by enhancing mitochondrial fusion and inhibiting mitophagy through suppression of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO) expression. Mechanistically, circSCMH1 exerted its inhibitory effect on KMO expression by binding to the transcription activator STAT5B, thereby impeding its nuclear translocation.
Conclusions: Our study reveals a novel mechanism by which circSCMH1 downregulates KMO expression, thereby enhancing mitochondrial fusion and inhibiting mitophagy, ultimately facilitating post-stroke brain repair. These findings shed new light on the role of circSCMH1 in promoting stroke recovery and underscore its potential as a therapeutic target for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: circSCMH1, functional recovery, ischemic stroke, KMO, STAT5B
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact