13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(2):219-230. doi:10.7150/thno.13178 This issue Cite
Research Paper
BET Bromodomain Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy in Ovarian Cancer by Downregulating FoxM1
1. State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Renji-Med X Clinical Stem Cell Research Center, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes, Shanghai Cancer Institute, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
3. GenenDesign Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China
4. State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology, School of Life Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian, China
5. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
6. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Gynecologic Oncology, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
7. School of Biomedical Engineering & Med-X Research Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
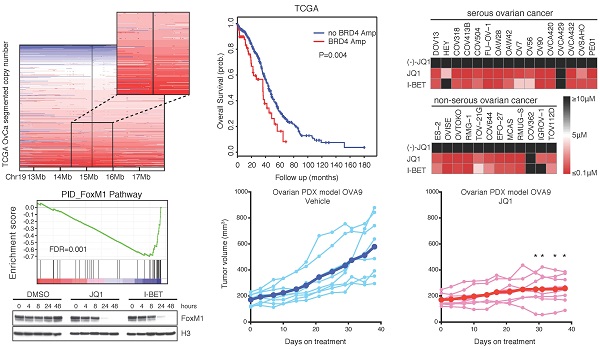
Ovarian cancer is responsible for the highest mortality among all gynecologic malignancies, and novel therapies are urgently needed to improve patient outcome. Here we performed an integrative genomic analysis and identified the bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) protein BRD4 as a potential therapeutic target in ovarian cancer. Suppression of BRD4 using small-molecule BET inhibitors JQ1 and I-BET151, or dual kinase-bromodomain inhibitor volasertib, led to robust and broad antitumor effects across all subclasses of ovarian cancer. In contrast to many other cancers which are susceptible to BET inhibition due to downregulation of super-enhancer-dependent MYC transcript, we discovered that JQ1-sensitive ovarian cancer cells exhibited marked disruption of Forkhead box protein M1 (FoxM1) pathway, a key driver of ovarian carcinoma. These in vitro findings were further supported by in vivo efficacies of JQ1 targeting both cell line-based and patient-derived xenograft models. Our data establish a new treatment strategy against ovarian cancer by employing epigenetic vulnerabilities, and provide a mechanistic rationale for the clinical investigation of BET bromodomain inhibitors in this deadly disease.
Keywords: ovarian cancer, BET inhibitors, BRD4, FoxM1
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact