13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(1):23-30. doi:10.7150/thno.16577 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Efficient Enhancement of Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability Using Acoustic Cluster Therapy (ACT)
1. Department of Physics, Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), Trondheim, Norway;
2. Phoenix Solutions AS, Oslo, Norway;
3. Department of Pathology and Medical Genetics, St. Olavs University Hospital, Trondheim, Norway;
4. Department of Laboratory Medicine, Children's and Women's Health, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway.
Abstract
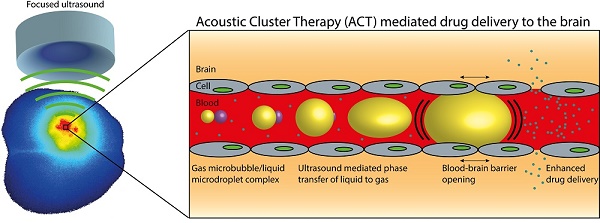
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a major obstacle in drug delivery for diseases of the brain, and today there is no standardized route to surpass it. One technique to locally and transiently disrupt the BBB, is focused ultrasound in combination with gas-filled microbubbles. However, the microbubbles used are typically developed for ultrasound imaging, not BBB disruption. Here we describe efficient opening of the BBB using the promising novel Acoustic Cluster Therapy (ACT), that recently has been used in combination with Abraxane® to successfully treat subcutaneous tumors of human prostate adenocarcinoma in mice. ACT is based on the conjugation of microbubbles to liquid oil microdroplets through electrostatic interactions. Upon activation in an ultrasound field, the microdroplet phase transfers to form a larger bubble that transiently lodges in the microvasculature. Further insonation induces volume oscillations of the activated bubble, which in turn induce biomechanical effects that increase the permeability of the BBB. ACT was able to safely and temporarily permeabilize the BBB, using an acoustic power 5-10 times lower than applied for conventional microbubbles, and successfully deliver small and large molecules into the brain.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier opening, focused ultrasound, acoustic cluster therapy (ACT), enhanced drug delivery
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact