13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(1):196-209. doi:10.7150/thno.27550 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles inhibit osteogenesis and exacerbate myeloma bone disease
1. Institute of Hematology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
2. Department of Bioinformatics and Systems Biology, Key Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics of the Ministry of Education, College of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
3. Department of Hematology, Wuhan Central Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
4. Department of Hematology, JingZhou Central Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Jingzhou, China.
5. Zhuhai People's Hospital of Jinan University, Zhuhai, China.
6. Department of Hematology, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China.
7. Department of Hematology, Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical College, Xinxiang, China.
8. Department of Hematology, Xiangyang Central Hospital, the Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang 441021, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
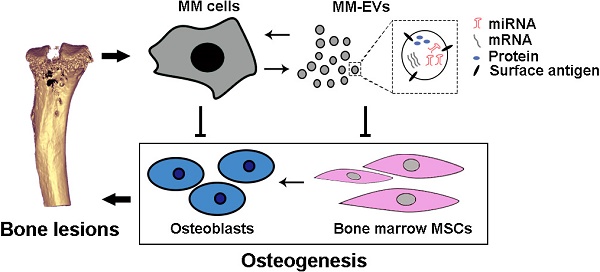
Background: As a hallmark driver of multiple myeloma (MM), MM bone disease (MBD) is unique in that it is characterized by severely impaired osteoblast activity resulting from blocked osteogenesis in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs). The mechanisms underlying this preferential blockade are incompletely understood.
Methods: miRNA expression of MM cell-derived extracellular vesicles (MM-EVs) was detected by RNA sequencing. MM-EVs impaired osteogenesis and exacerbated MBD were in vitro and in vivo validated by histochemical staining, qPCR and micro-CT. We additionally examined the correlation between CD138+ circulating EVs (cirEVs) count and bone lesion in de novo MM patients.
Results: Here, by sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, we found that MM-EVs were enriched in various molecules negatively regulating osteogenesis. We experimentally verified that MM-EVs inhibited BM-MSC osteogenesis, induced elevated expression of miR-103a-3p inhibiting osteogenesis in BM-MSCs, and increased cell viability and interleukin-6 secretion in MM cells. In a mouse model, MM-EVs that were injected into the marrow space of the left tibia led to impaired osteogenesis and exacerbated MBD and MM progression. Furthermore, the levels of CD138+ cirEVs in the peripheral blood were positively correlated with the number of MM bone lesions in MM patients.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that MM-EVs play a pivotal role in the development of severely impaired osteoblast activity, which represents a novel biomarker for the precise diagnosis of MBD and a compelling rationale for exploring MM-EVs as a therapeutic target.
Keywords: multiple myeloma, extracellular vesicles, mesenchymal stem cells, osteogenesis, bone lesions
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact