13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(23):6949-6961. doi:10.7150/thno.38061 This issue Cite
Research Paper
3D-bioprinting a genetically inspired cartilage scaffold with GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden hydrogel and polymer for cartilage repair
1. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Orthopedic Implants, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, 200011, China.
2. Department of Nephrology, Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, North District of Suzhou Municipal Hospital, Suzhou, China.
*Ye Sun and Yongqing You contributed equally to the article.
Abstract
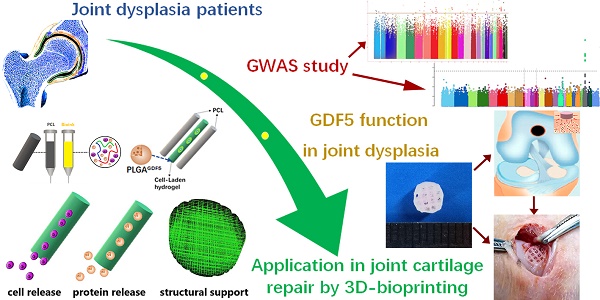
Rationale: Articular cartilage injury is extremely common in congenital joint dysplasia patients. Genetic studies have identified Growth differentiation factor 5 (GDF5) as a shared gene in joint dysplasia and OA progression across different populations. However, few studies have employed GDF5 in biological regeneration for articular cartilage repair.
Methods & Results: In the present study, we report identified genetic association between GDF5 loci and hip joint dysplasia with genome-wide association study (GWAS). GWAS and replication studies in separate populations achieved significant signals for GDF5 loci. GDF5 expression was dysregulated with allelic differences in hip cartilage of DDH and upregulated in the repaired cartilage in a rabbit cartilage defect model. GDF5 in vitro enhanced chondrogenesis and migration of bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs), GDF5 was tested in ectopic cartilage generation with BMSCs by GDF5 in nude mice in vivo. Genetically inspired, we further generated functional knee articular cartilage construct for cartilage repair by 3d-bioprinting a GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden scaffold. GDF5-conjugated scaffold showed better cartilage repairing effects compared to control. Meanwhile, transplantation of the 3D-bioprinted GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden scaffold in rabbit knees conferred long-term chondroprotection.
Conclusions: In conclusion, we report identified genetic association between GDF5 and DDH with combined GWAS and replications, which further inspired us to generate a ready-to-implant GDF5-conjugated BMSC-laden scaffold with one-step 3d-bioprinting for cartilage repair.
Keywords: joint dysplasia, genetics, 3d-bioprinting, hydrogel, tissue engineering
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact