13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(24):7210-7221. doi:10.7150/thno.36525 This issue Cite
Research Paper
AIEgens Barcodes Combined with AIEgens Nanobeads for High-sensitivity Multiplexed Detection
1. State Key Lab of Metal Matrix Composites, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, China
2. The First People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong Uni-versity, 100 Haining Road, Shanghai, 200080, P. R. China
3. Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Shanghai 200092, PR China
4. Institute of Nano Biomedicine and Engineering, Key Laboratory of Thin Film and Microfabrication Technology of Ministry of Education, Department ofInstrument Science and Engineering, School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, National Center for Translational Medicine, CollaborativeInnovational Center for System Biology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai 200240, PR China
5. Laboratory of Molecular Imaging and Nanomedicine (LOMIN), National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, Maryland 20892, United States
Abstract
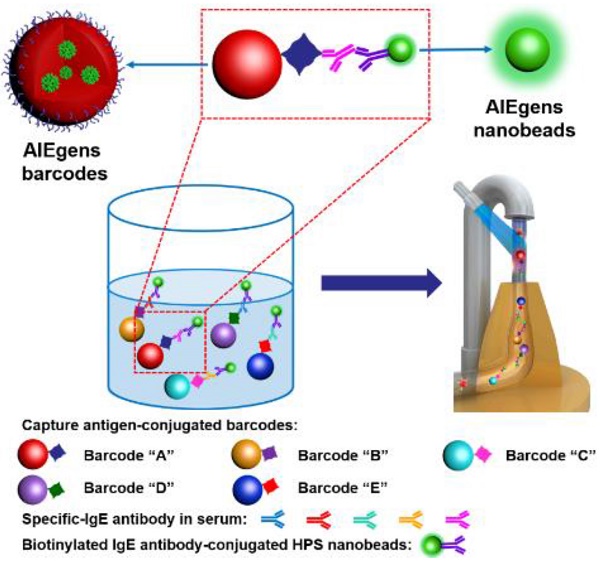
Suspension arrays based on optical encoded microspheres have attracted great attention for multiplexed detection in gene analysis, protein profiling, early disease diagnosis, treatment monitoring and so on. However, the fluorescence stability of barcodes and detection sensitivity require further improvement to meet the increasing demands of “precision diagnosis”. Methods: This work reports a novel suspension array platform based on extremely stable AIEgens (AIE33 and AIE NIR800) microbeads as barcodes and AIEgens (1,1,2,3,4,5-Hexaphenyl-1H-silole, HPS) nanobeads as fluorescent signal reporter coupled with flow cytometry for multiplexed detection. Results: Due to the excellent fluorescent signal amplification effect of the HPS nanobeads, our multiplex assay showed enhanced detection sensitivity, compared to multiplex assay using QDs nanobeads (up to 3-fold improvement) and commercial organic dye of phycoerythrin (up to 5-fold improvement) as the fluorescent signal reporters. Conclusion: Furthermore, validating experiments showed similar detection performance to the clinical gold-standard method of ImmunoCAP for allergen detection in patient serum samples, demonstrating the suspension array platform based on AIEgens microbeads with excellent fluorescence stability and AIEgens nanobeads with strong signal amplification ability is promising for high-sensitivity multiplexed bioassay applications.
Keywords: Aggregation-induced emission (AIE), AIEgens barcodes, AIEgens nanobeads, multiplexed detection, allergens
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact