13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(26):8196-8205. doi:10.7150/thno.36455 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Optogenetic control of mesenchymal cell fate towards precise bone regeneration
1. Guanghua School of Stomatology, Hospital of Stomatology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Sun Yat-sen University, 56 Lingyuanxi Road, Guangzhou 510055, China.
Abstract
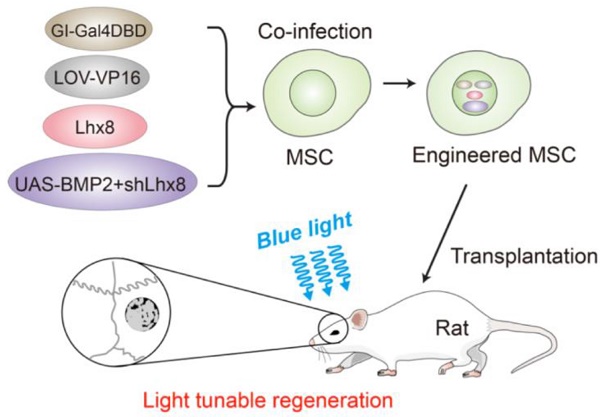
Rationale: Spatial-temporal control of cell fate in vivo is of great importance for regenerative medicine. Currently, there remain no practical strategies to tune cell-fate spatial-temporally. Optogenetics is a biological technique that widely used to control cell activity in genetically defined neurons in a spatiotemporal-specific manner by light. In this study, optogenetics was repurposed for precise bone tissue regeneration.
Methods: Lhx8 and BMP2 genes, which are considered as the master genes for mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation respectively, were recombined into a customized optogenetic control system. In the system, Lhx8 was constitutively expressed, while BMP2 together with shLhx8 expression was driven by blue light.
Results: As expected, blue light induced BMP2 expression and inactivated Lhx8 expression in cells infected with the optogenetic control system. Optogenetic control of BMP2 and Lhx8 expression inversely regulates MSC fate in vitro. By animal study, we found that blue light could fine-tune the regeneration in vivo. Blue light illumination significantly promotes bone regeneration when the scaffold was loaded with MSCs infected with adeno-Lhx8, GI-Gal4DBD, LOV-VP16, and BMP2-shLhx8.
Conclusions: Together, our study revealed that optogenetic control of the master genes for mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation would be such a candidate strategy for precise regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Optogenetics, bone tissue regeneration, gene expression control, proliferation and differentiation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact