13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(4):1719-1732. doi:10.7150/thno.37049 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Silica Perturbs Primary Cilia and Causes Myofibroblast Differentiation during Silicosis by Reduction of the KIF3A-Repressor GLI3 Complex
1. Medical Research Center, Hebei Key Laboratory for Organ Fibrosis Research, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China
2. Basic Medicine College, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China
3. College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China
4. School of Public Health, North China University of Science and Technology, Tangshan, China
5. Department of Neurosurgery, Tangshan People's Hospital, Tangshan, China
6. Basic Medical College, Xiamen Medical Collage, Xiamen, China
Abstract
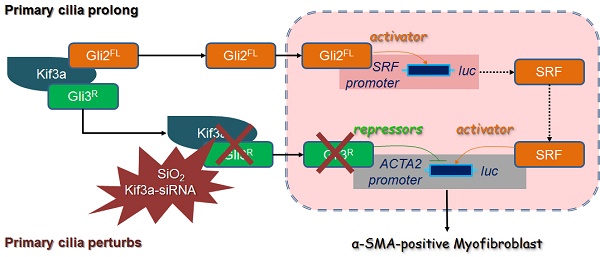
The purpose of this study was to determine the effects of Kinesin family member 3A (KIF3A) on primary cilia and myofibroblast differentiation during silicosis by regulating Sonic hedgehog (SHH) signalling.
Methods: Changes in primary cilia during silicosis and myofibroblast differentiation were detected in silicotic patients, experimental silicotic rats, and a myofibroblast differentiation model induced by SiO2. We also explored the mechanisms underlying KIF3A regulation of Glioma-associated oncogene homologs (GLIs) involved in myofibroblast differentiation.
Results: Primary cilia (marked by ARL13B and Ac-α-Tub) and ciliary-related proteins (IFT 88 and KIF3A) were increased initially and then decreased as silicosis progressed. Loss and shedding of primary cilia were also found during silicosis. Treatment of MRC-5 fibroblasts with silica and then transfection of KIF3A-siRNA blocked activation of SHH signalling, but increased GLI2FL as a transcriptional activator of SRF, and reduced the inhibitory effect of GLI3R on ACTA2.
Conclusion: Our findings indicate that primary cilia are markedly altered during silicosis and the loss of KIF3A may promote myofibroblast differentiation induced by SiO2.
Keywords: Primary cilia, Kinesin family member 3A, Glioma-associated oncogene homolog 3, silicosis, fibroblast
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact