13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(14):6500-6516. doi:10.7150/thno.44113 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Depletion of the diabetic gut microbiota resistance enhances stem cells therapy in type 1 diabetes mellitus
1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, 22 Zhongguancun Nandajie, Haidian District, Beijing 100081, People's Republic of China
2. Department of Periodontics, School of Dental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, USA
3. Peking University Hospital of Stomatology First Clinical Division, 37 Xishikudajie, Xicheng District, Beijing 100034, People's Republic of China
4. Institute for Immunology and Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Beijing Key Lab for Immunological Research on Chronic Diseases, School of Medicine; Tsinghua-Peking Center for Life Sciences, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, People's Republic of China
5. Department of Geriatric Dentistry, National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing Laboratory of Biomedical Materials, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Peking University, Beijing 100081, People's Republic of China
6. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, 22 Zhongguancun Nandajie, Haidian District, Beijing 100081, People's Republic of China
7. The First People's Hospital of Jinzhong, ShanXi Province 030600, People's Republic of China
Abstract
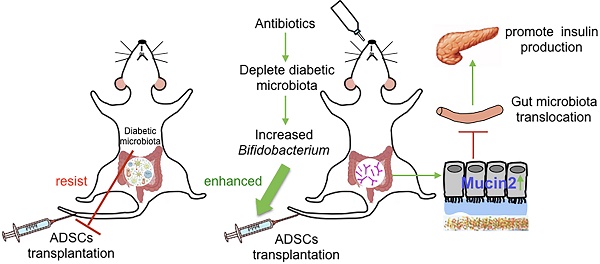
Microbiome, considered as the “second genome” of the host, is altered in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) patients to a state of dysbiosis. Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) transplantation is a promising treatment for T1DM but is limited by several factors in the diabetic host. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that dysbiotic gut microbiota may limit MSC therapy, and modulating gut microbiota may help to improve the effects of MSC transplantation.
Methods: NOD/Ltj mice, treated with adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), were fed with an antibiotics cocktails (Abx) for 1 week. The blood glucose levels, insulitis, intestinal permeability and gut bacteria translocation to the pancreas were evaluated. 16s rRNA and colon tissue transcription sequencing were performed to analyze beneficial bacteria and reactive host biomolecules in the ADSCs+Abx group. Based on the sequencing results, specific bacteria were gavaged orally to diabetic mice to confirm their effect on ADSCs transplantation in T1DM was determined.
Results: We found that the recolonized the diabetic gut microbiota abolished the therapeutic effect of ADSCs. On the contrary, depletion of the diabetic gut microbiota by antibiotics treatment in diabetic mice significantly enhanced the therapeutic effects of ADSCs as measured by reversal of hyperglycemia, insulitis, and increased insulin output. Mechanistically, treatment with antibiotics increased the abundance of Bifidobacterium in the gut and reduced bacterial translocation to the pancreas by promoting Mucin2 expression and thickening the mucus layer through TRPM7. The mechanism was confirmed the re-colonization of the gut by B.breve through oral gavage that produced similar results.
Conclusions: These results provide the rationale for a new approach to improve MSC therapy for T1DM by altering the gut microbiota.
Keywords: Type 1 diabetes mellitus, Stem cell transplantation, Broad-spectrum antibiotics, Gut microbiota translocation, Bifidobacterium
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact