13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(1):64-78. doi:10.7150/thno.46124 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Extracellular-vesicles delivered tumor-specific sequential nanocatalysts can be used for MRI-informed nanocatalytic Therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200438, P. R. China.
2. School of Life Sciences, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, P. R. China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Background: Conventional therapeutic strategies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains a great challenge, therefore the alternative therapeutic modality for specific and efficient HCC suppression is urgently needed.
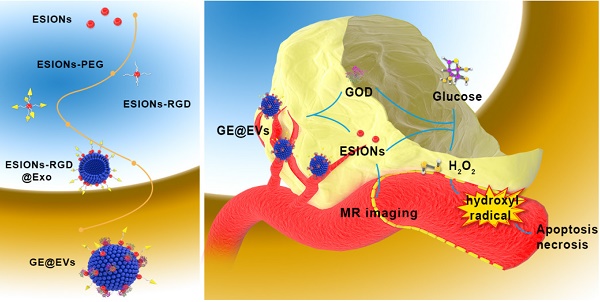
Methods: In this work, HCC-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) were applied as surface nanocarrier for sequential nanocatalysts GOD-ESIONs@EVs (GE@EVs) of tumor-specific and cascade nanocatalytic therapy against HCC. By enhancing the intracellular endocytosis through arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD)-targeting effect and membrane fusion, sequential nanocatalysts led to more efficient treatment in the HCC tumor region in a shorter period of time.
Results: Through glucose consumption as catalyzed by the loaded glucose oxidase (GOD) to overproduce hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), highly toxic hydroxyl radicals were generated by Fenton-like reaction as catalyzed by ESIONs, which was achieved under the mildly acidic tumor microenvironment, enabling the stimuli of the apoptosis and necrosis of HCC cells. This strategy demonstrated the high active-targeting capability of GE@EVs into HCC, achieving highly efficient tumor suppression both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, the as-synthesized nanoreactor could act as a desirable nanoscale contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging, which exhibited desirable imaging capability during the sequential nanocatalytic treatment.
Conclusion: This application of surface-engineering EVs not only proves the high-performance catalytic therapeutic modality of GE@EVs for HCC, but also broadens the versatile bio-applications of EVs.
Keywords: extracellular vesicles, catalytic nanomedicine, theranostics, hepatocellular carcinoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact