13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(5):2263-2277. doi:10.7150/thno.51571 This issue Cite
Review
Targeted delivery of extracellular vesicles in heart injury
1. Laboratory of Heart Center and Department of Cardiology, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
2. Guangdong Provincial Biomedical Engineering Technology Research Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Guangzhou, China.
3. Laboratory of Heart Center, Sino-Japanese Cooperation Platform for Translational Research in Heart Failure, Guangzhou, China.
4. Biomaterials Research Center, School of Biomedical Engineering, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China.
Abstract
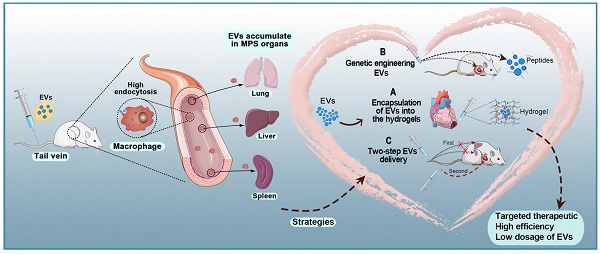
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale extracellular vesicles derived from endocytosis that are crucial to intercellular communication. EVs possess natural biocompatibility and stability that allow them to cross biological membranes and that protect them from degradation. Recent studies have shown that EVs-mediated crosstalk between different cell types in the heart could play important roles in the maintenance of cardiac homeostasis and the pathogenesis of heart diseases. In particular, EVs secreted by different types of stem cells exhibit cardioprotective effects. However, numerous studies have shown that intravenously injected EVs are quickly cleared by macrophages of the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) and preferentially accumulate in MPS organs such as the liver, spleen, and lung. In this review, we discuss exosome biogenesis, the role of EVs in heart diseases, and challenges in delivering EVs to the heart. Furthermore, we extensively discuss the targeted delivery of EVs for treating ischemic heart disease. These understandings will aid in the development of effective treatment strategies for heart diseases.
Keywords: Extracellular Vesicles, Biogenesis, Heart Injury, Challenges, Targeted Delivery
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact