13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(7):3213-3228. doi:10.7150/thno.52010 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Prussian blue nanozyme-mediated nanoscavenger ameliorates acute pancreatitis via inhibiting TLRs/NF-κB signaling pathway
1. Department of Ultrasound in Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai, 200233, P. R. China
2. Department of Gastroenterology, Changhai Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, P. R. China.
3. Shanghai Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai, 200233, P. R. China.
4. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Ultrasound Molecular Imaging, Ultrasound Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University. Chongqing 400010, P. R. China.
* Xue Xie, Jiulong Zhao and Wei Gao contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
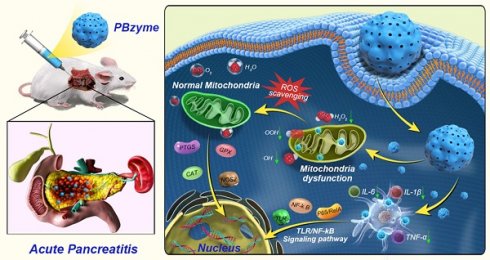
Rationale: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a serious acute condition affecting the abdomen and shows high morbidity and mortality rates. Its global incidence has increased in recent years. Inflammation and oxidative stress are potential therapeutic targets for AP. This study was conducted to investigate the intrinsic anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of Prussian blue nanozyme (PBzyme) on AP, along with its underlying mechanism.
Methods: Prussian blue nanozymes were prepared by polyvinylpyrrolidone modification method. The effect of PBzyme on inhibiting inflammation and scavenging reactive oxygen species was verified at the cellular level. The efficacy and mechanism of PBzyme for prophylactically treating AP were evaluated using the following methods: serum testing in vivo, histological scoring following hematoxylin and eosin staining, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling fluorescence staining, polymerase chain reaction array, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis and Western blotting analysis.
Results: The synthetic PBzyme showed potent anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects in reducing oxidative stress and alleviating inflammation both in vitro and in vivo in the prophylactic treatment of AP. The prophylactic therapeutic efficacy of PBzyme on AP may involve inhibition of the toll-like receptor/nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway and reactive oxygen species scavenging.
Conclusion: The single-component, gram-level mass production, stable intrinsic biological activity, biosafety, and good therapeutic efficacy suggest the potential of PBzyme in the preventive treatment of AP. This study provides a foundation for the clinical application of PBzyme.
Keywords: prussian blue nanozyme, acute pancreatitis, inflammation, reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact