13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(16):7995-8007. doi:10.7150/thno.50990 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ablation of lncRNA Miat attenuates pathological hypertrophy and heart failure
1. Molecular Cardiology Program, Department of Biomedical Engineering, University of Alabama at Birmingham, School of Medicine and School of Engineering, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA.
2. Feinberg Cardiovascular Research Institute, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL 60611, USA.
3. Department of Cardiology, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China.
4. Department of Medicine, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA
5. Department of Stem Cell Biology, Atomic Bomb Disease Institute, Nagasaki University, Nagasaki 852-8523, Japan.
6. Center for Molecular and Translational Medicine, Institute of Biomedical Science, Georgia State University, Atlanta, GA 30303, USA.
7. Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-0812, Japan.
8. Solomon H. Snyder Department of Neuroscience, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
Abstract
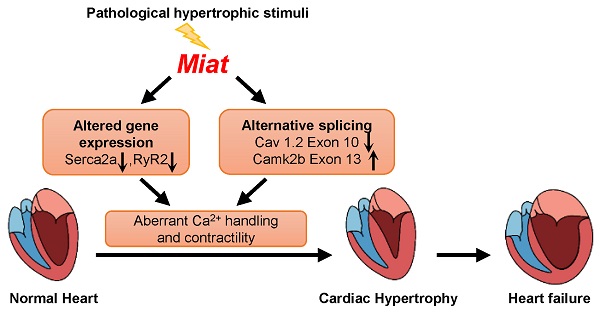
Rationale: The conserved long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) myocardial infarction associate transcript (Miat) was identified for its multiple single-nucleotide polymorphisms that are strongly associated with susceptibility to MI, but its role in cardiovascular biology remains elusive. Here we investigated whether Miat regulates cardiac response to pathological hypertrophic stimuli.
Methods: Both an angiotensin II (Ang II) infusion model and a transverse aortic constriction (TAC) model were used in adult WT and Miat-null knockout (Miat-KO) mice to induce pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Heart structure and function were evaluated by echocardiography and histological assessments. Gene expression in the heart was evaluated by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq), quantitative real-time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR), and Western blotting. Primary WT and Miat-KO mouse cardiomyocytes were isolated and used in Ca2+ transient and contractility measurements.
Results: Continuous Ang II infusion for 4 weeks induced concentric hypertrophy in WT mice, but to a lesser extent in Miat-KO mice. Surgical TAC for 6 weeks resulted in decreased systolic function and heart failure in WT mice but not in Miat-KO mice. In both models, Miat-KO mice displayed reduced heart-weight to tibia-length ratio, cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and cardiac interstitial fibrosis and a better-preserved capillary density, as compared to WT mice. In addition, Ang II treatment led to significantly reduced mRNA and protein expression of the Ca2+ cycling genes Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase 2a (SERCA2a) and ryanodine receptor 2 (RyR2) and a dramatic increase in global RNA splicing events in the left ventricle (LV) of WT mice, and these changes were largely blunted in Miat-KO mice. Consistently, cardiomyocytes isolated from Miat-KO mice demonstrated more efficient Ca2+ cycling and greater contractility.
Conclusions: Ablation of Miat attenuates pathological hypertrophy and heart failure, in part, by enhancing cardiomyocyte contractility.
Keywords: lncRNA, Miat, cardiac hypertrophy, heart failure, RNA splicing, cardiomyocytes
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact