13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2021; 11(20):9873-9883. doi:10.7150/thno.59418 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Biological relevance of Granzymes A and K during E. coli sepsis
1. Fundación Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Aragón (IIS Aragón), Biomedical Research Centre of Aragón (CIBA), 50009, Zaragoza, Spain.
2. Animal Unit, University of Zaragoza, 50009, Zaragoza, Spain.
3. Instituto de Carboquímica ICB-CSIC, 50018, Zaragoza, Spain.
4. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Biomedicine Discovery Institute, Monash University, 3800, Clayton VIC, Australia.
5. Aragon I+D Foundation (ARAID), 50018, Zaragoza, Spain.
6. Nanoscience Institute of Aragon (INA), University of Zaragoza, 50018, Zaragoza, Spain.
7. Department of Microbiology, Preventive Medicine and Public Health, University of Zaragoza, 50009, Zaragoza, Spain.
8. San Jorge University, 50830, Zaragoza, Spain.
*Contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
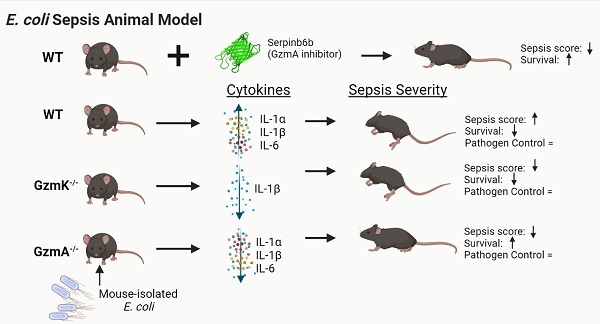
Aims: Recent in vitro findings suggest that the serine protease Granzyme K (GzmK) may act as a proinflammatory mediator. However, its role in sepsis is unknown. Here we aim to understand the role of GzmK in a mouse model of bacterial sepsis and compare it to the biological relevance of Granzyme A (GzmA).
Methods: Sepsis was induced in WT, GzmA-/- and GzmK-/- mice by an intraperitoneal injection of 2x108 CFU from E. coli. Mouse survival was monitored during 5 days. Levels of IL-1α, IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6 in plasma were measured and bacterial load in blood, liver and spleen was analyzed. Finally, profile of cellular expression of GzmA and GzmK was analyzed by FACS.
Results: GzmA and GzmK are not involved in the control of bacterial infection. However, GzmA and GzmK deficient mice showed a lower sepsis score in comparison with WT mice, although only GzmA deficient mice exhibited increased survival. GzmA deficient mice also showed reduced expression of some proinflammatory cytokines like IL1-α, IL-β and IL-6. A similar result was found when extracellular GzmA was therapeutically inhibited in WT mice using serpinb6b, which improved survival and reduced IL-6 expression. Mechanistically, active extracellular GzmA induces the production of IL-6 in macrophages by a mechanism dependent on TLR4 and MyD88.
Conclusions: These results suggest that although both proteases contribute to the clinical signs of E. coli-induced sepsis, inhibition of GzmA is sufficient to reduce inflammation and improve survival irrespectively of the presence of other inflammatory granzymes, like GzmK.
Keywords: Granzyme K, Granzyme A, bacterial sepsis, inflammation
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact