13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(1):105-125. doi:10.7150/thno.63788 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A novel C-terminal heat shock protein 90 inhibitor that overcomes STAT3-Wnt-β-catenin signaling-mediated drug resistance and adverse effects
1. Creative Research Initiative Center for concurrent control of emphysema and lung cancer, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea.
2. College of Pharmacy and Research Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Molecular Medicine and Biopharmaceutical Sciences, Graduate School of Convergence Science and Technology and College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, Seoul 08826, Republic of Korea.
4. School of Pharmacy, Sungkyunkwan University, Suwon, Gyeonggi-do 16419, Republic of Korea.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
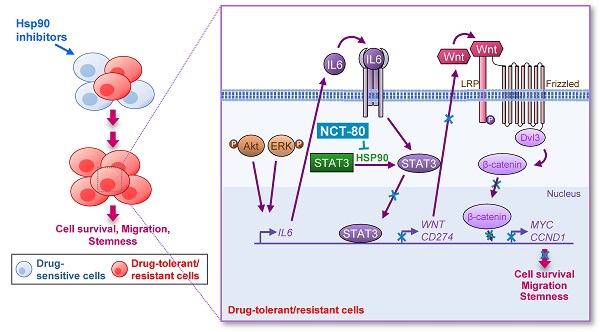
Rationale: The heat shock protein (Hsp) system plays important roles in cancer stem cell (CSC) and non-CSC populations. However, limited efficacy due to drug resistance and toxicity are obstacles to clinical use of Hsp90 inhibitors, suggesting the necessity to develop novel Hsp90 inhibitors overcoming these limitations.
Methods: The underlying mechanism of resistance to Hsp90 inhibitors was investigated by colony formation assay, sphere formation assay, western blot analysis, and real-time PCR. To develop anticancer Hsp90 inhibitors that overcome the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3)-mediated resistance, we synthesized and screened a series of synthetic deguelin-based compounds in terms of inhibition of colony formation, migration, and viability of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and toxicity to normal cells. Regulation of Hsp90 by the selected compound NCT-80 [5-methoxy-N-(3-methoxy-4-(2-(pyridin-3-yl)ethoxy)phenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2H-chromene-6-carboxamide] was investigated by immunoprecipitation, drug affinity responsive target stability assay, binding experiments using ATP-agarose beads and biotinylated drug, and docking analysis. The antitumor, antimetastatic, and anti-CSC effects of NCT-80 were examined in vitro and in vivo using various assays such as MTT, colony formation, and migration assays and flow cytometric analysis and tumor xenograft models.
Results: We demonstrated a distinct mechanism in which Hsp90 inhibitors that block N-terminal ATP-binding pocket causes transcriptional upregulation of Wnt ligands through Akt- and ERK-mediated activation of STAT3, resulting in NSCLC cell survival in an autocrine or paracrine manner. In addition, NCT-80 effectively reduced viability, colony formation, migration, and CSC-like phenotypes of NSCLC cells and their sublines with acquired resistance to anticancer drugs by inducing apoptosis and inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the growth of NSCLC patient-derived xenograft tumors without overt toxicity. With regards to mechanism, NCT-80 directly bound to the C-terminal ATP-binding pocket of Hsp90, disrupting the interaction between Hsp90 and STAT3 and degrading STAT3 protein. Moreover, NCT-80 inhibited chemotherapy- and EGFR TKI-induced programmed cell death ligand 1 expression and potentiated the antitumor effect of chemotherapy in the LLC-Luc allograft model.
Conclusions: These data indicate the potential of STAT3/Wnt signaling pathway as a target to overcome resistance to Hsp90 inhibitors and NCT-80 as a novel Hsp90 inhibitor that targets both CSCs and non-CSCs in NSCLC.
Keywords: heat shock protein 90, antitumor, deguelin, drug resistance
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact