13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(2):704-723. doi:10.7150/thno.80184 This issue Cite
Review
Battles against aberrant KEAP1-NRF2 signaling in lung cancer: intertwined metabolic and immune networks
1. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200030, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Anhui Chest Hospital, Hefei, 230000, China
3. Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard University; Boston, MA 02115, USA.
4. Division of General Thoracic Surgery, Department of BioMedical Research (DBMR), Inselspital, Bern University Hospital, University of Bern; Bern, 3010, Switzerland.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
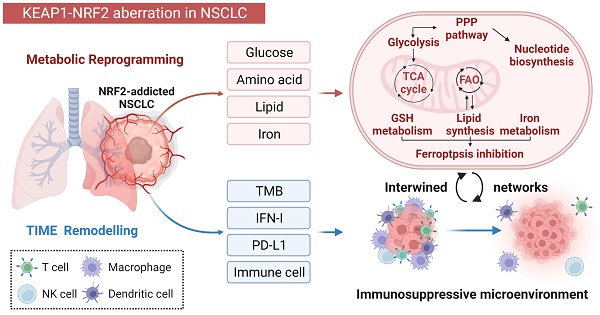
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1/nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 (KEAP1/NRF2) pathway is well recognized as a key regulator of redox homeostasis, protecting cells from oxidative stress and xenobiotics under physiological circumstances. Cancer cells often hijack this pathway during initiation and progression, with aberrant KEAP1-NRF2 activity predominantly observed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), suggesting that cell/tissue-of-origin is likely to influence the genetic selection during malignant transformation. Hyperactivation of NRF2 confers a multi-faceted role, and recently, increasing evidence shows that a close interplay between metabolic reprogramming and tumor immunity remodelling contributes to its aggressiveness, treatment resistance (radio-/chemo-/immune-therapy) and susceptibility to metastases. Here, we discuss in detail the special metabolic and immune fitness enabled by KEAP1-NRF2 aberration in NSCLC. Furthermore, we summarize the similarities and differences in the dysregulated KEAP1-NRF2 pathway between two major histo-subtypes of NSCLC, provide mechanistic insights on the poor response to immunotherapy despite their high immunogenicity, and outline evolving strategies to treat this recalcitrant cancer subset. Finally, we integrate bioinformatic analysis of publicly available datasets to illustrate the new partners/effectors in NRF2-addicted cancer cells, which may provide new insights into context-directed treatment.
Keywords: KEAP1-NRF2 signaling, non-small cell lung cancer, metabolic reprogramming, tumor immune microenvironment, bioinformatics, therapeutic vulnerabilities
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact