13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(7):2241-2255. doi:10.7150/thno.78426 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Small extracellular vesicle-loaded bevacizumab reduces the frequency of intravitreal injection required for diabetic retinopathy
1. Centre for Molecular Neurosciences, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
2. Department of Ophthalmology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
3. Centre for Biotherapeutics Research, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
4. Department of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
5. Department of Pharmacology, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
6. Department of Pathology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
7. Divison of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO 65211, USA.
8. Institute for Regenerative Medicine, Department of Molecular and Cellular Medicine, College of Medicine, Texas A&M University Health Science Center, College Station, TX, United States.
9. Department of Pharmacology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, 576104, India.
Abstract
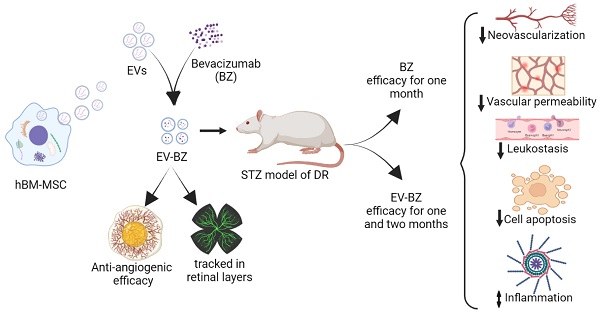
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is associated with retinal neovascularization, hard exudates, inflammation, oxidative stress and cell death, leading to vision loss. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (Anti-VEGF) therapy through repeated intravitreal injections is an established treatment for reducing VEGF levels in the retina for inhibiting neovascularization and leakage of hard exudates to prevent vision loss. Although anti-VEGF therapy has several clinical benefits, its monthly injection potentially causes devastating ocular complications, including trauma, intraocular hemorrhage, retinal detachment, endophthalmitis, etc.
Methods: As mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and MSC-derived extracellular vesicles (MSC-EVs) demonstrated safety in clinical studies, we have tested the efficacy of MSC-derived small EVs (MSC-sEVs) loaded anti-VEGF drug bevacizumab in a rat model of DR.
Results: The study identified a clinically significant finding that sEV loaded with bevacizumab reduces the frequency of intravitreal injection required for treating diabetic retinopathy. The sustained effect is observed from the reduced levels of VEGF, exudates and leukostasis for more than two months following intravitreal injection of sEV loaded with bevacizumab, while bevacizumab alone could maintain reduced levels for about one month. Furthermore, retinal cell death was consistently lower in this period than only bevacizumab.
Conclusion: This study provided significant evidence for the prolonged benefits of sEVs as a drug delivery system. Also, EV-mediated drug delivery systems could be considered for clinical application of retinal diseases as they maintain vitreous clarity in the light path due to their composition being similar to cells.
Keywords: Diabetic retinopathy, extracellular vesicles, bevacizumab, intravitreal injection, neovascularization.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact