13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(7):2281-2300. doi:10.7150/thno.82431 This issue Cite
Review
Targeting HSF1 for cancer treatment: mechanisms and inhibitor development
1. Graduate Institute of Biomedical Sciences and Research Center for Cancer Biology, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
2. The Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Medical Faculty, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia.
3. Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Taichung Veterans General Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
4. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, College of Medicine, University of Florida, Gainesville, USA.
5. Cancer Research Institute and School of Basic Medical Sciences, Central South University, Changsha, China.
6. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Warren Alpert Medical School & Legorreta Cancer Center, Brown University, Providence, USA.
7. Institute of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, R.O.C.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
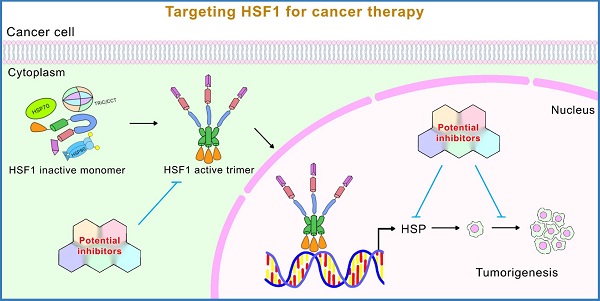
Heat Shock Factor 1 (HSF1) is a master regulator of heat shock responsive signaling. In addition to playing critical roles in cellular heat shock response, emerging evidence suggests that HSF1 also regulates a non-heat shock responsive transcriptional network to handle metabolic, chemical, and genetic stress. The function of HSF1 in cellular transformation and cancer development has been extensively studied in recent years. Due to important roles for HSF1 for coping with various stressful cellular states, research on HSF1 has been very active. New functions and molecular mechanisms underlying these functions have been continuously discovered, providing new targets for novel cancer treatment strategies. In this article, we review the essential roles and mechanisms of HSF1 action in cancer cells, focusing more on recently discovered functions and their underlying mechanisms to reflect the new advances in cancer biology. In addition, we emphasize new advances with regard to HSF1 inhibitors for cancer drug development.
Keywords: HSF1, Heat shock response, cellular stress, cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact