13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(12):4266-4286. doi:10.7150/thno.84971 This issue Cite
Review
Engineering strategies and optimized delivery of exosomes for theranostic application in nerve tissue
1. Department of Trauma and Orthopedics, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100000, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Trauma and Neural Regeneration (Peking University), Ministry of Education, Beijing 100000, China.
3. National Center for Trauma Medicine, Beijing 100000, China.
4. Department of Central Laboratory and Institute of Clinical Molecular Biology, Peking University People's Hospital, Beijing 100000, China.
Abstract
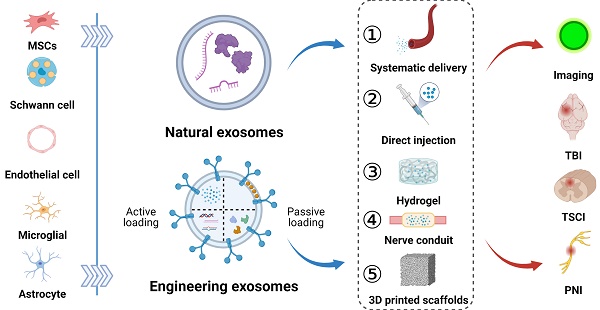
Severe injuries or diseases affecting the peripheral and central nervous systems can result in impaired organ function and permanent paralysis. Conventional interventions, such as drug administration and cell-based therapy, exhibit limited effectiveness due to their inability to preserve post-implantation cell survival and impede the deterioration of adjacent tissues. Exosomes have recently emerged as powerful tools for tissue repair owing to their proteins and nucleic acids, as well as their unique phospholipid properties, which facilitate targeted delivery to recipient cells. Engineering exosomes, obtained by manipulating the parental cells or directly functionalizing exosomes, play critical roles in enhancing regenerative repair, reducing inflammation, and maintaining physiological homeostasis. Furthermore, exosomes have been shown to restore neurological function when used in combination with biomaterials. This paper primarily focuses on the engineering strategies and delivery routes of exosomes related to neural research and emphasizes the theranostic application of optimized exosomes in peripheral nerve, traumatic spinal cord, and brain injuries. Finally, the prospects of exosomes development and their combination with other approaches will be discussed to enhance our knowledge on their theranostic effectiveness in neurological diseases.
Keywords: biomaterials, engineering exosomes, exosomal miRNA, nerve injury, neuroimaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact