13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(3):661-675. doi:10.7150/thno.27794 This issue Cite
Research Paper
VEGFC acts as a double-edged sword in renal cell carcinoma aggressiveness
1. University of Nice Sophia Antipolis, Institute for research on cancer and aging of Nice, CNRS UMR 7284; INSERM U1081, Centre Antoine Lacassagne, France
2. Centre Scientifique de Monaco, Biomedical Department, 8 Quai Antoine Ier, MC-98000 Monaco, Principality of Monaco.
3. Université Paris Descartes, Sorbonne Paris Cité, INSERM U1016, Institut Cochin, Paris, 75014 France; CNRS UMR 8104, Paris, 75014 France, Paris, 75014 France.
4. Nice University Hospital, Central laboratory of Pathology.
5. Rennes University, Rennes University Hospital, Department of Pathology, Rennes, France.
Abstract
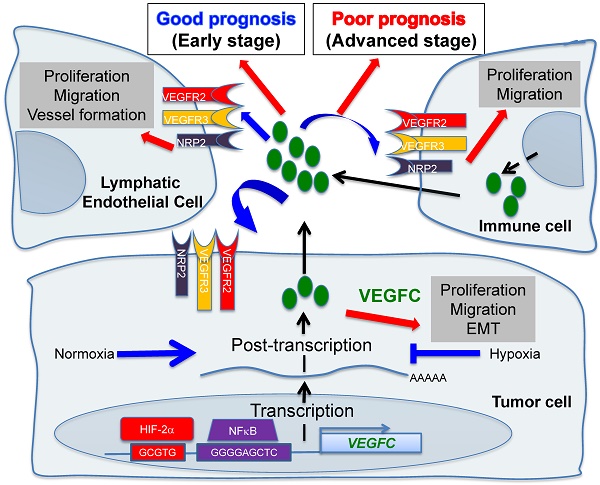
Hypoxic zones are common features of metastatic tumors. Due to inactivation of the von Hippel-Lindau gene (VHL), renal cell carcinomas (RCC) show constitutive stabilization of the alpha subunit of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF). Thus, RCC represents a model of chronic hypoxia. Development of the lymphatic network is dependent on vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) and lies at the front line of metastatic spreading. Here, we addressed the role of VEGFC in RCC aggressiveness and the regulation of its expression in hypoxia.
Methods: Transcriptional and post transcriptional regulation of VEGFC expression was evaluated by qPCR and with reporter genes. The involvement of HIF was evaluated using a siRNA approach. Experimental RCC were performed with immuno-competent/deficient mice using human and mouse cells knocked-out for the VEGFC gene by a CRISPR/Cas9 method. The VEGFC axis was analyzed with an online available data base (TCGA) and using an independent cohort of patients.
Results: Hypoxia induced VEGFC protein expression but down-regulated VEGFC gene transcription and mRNA stability. Increased proliferation, migration, over-activation of the AKT signaling pathway and enhanced expression of mesenchymal markers characterized VEGFC-/- cells. VEGFC-/- cells did not form tumors in immuno-deficient mice but developed aggressive tumors in immuno-competent mice. These tumors showed down-regulation of markers of activated lymphocytes and M1 macrophages, and up-regulation of M2 macrophages markers and programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1). Over-expression of lymphangiogenic genes including VEGFC was linked to increased disease-free and overall survival in patients with non-metastatic tumors, whereas its over-expression correlated with decreased progression-free and overall survival of metastatic patients.
Conclusion: Our study revisited the admitted dogma linking VEGFC to tumor aggressiveness. We conclude that targeting VEGFC for therapy must be considered with caution.
Keywords: VEGFC, lymphangiogenesis, sunitinib, angiogenesis, renal cell carcinoma, metastasis, CRISPR/Cas9
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact