13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(10):4466-4480. doi:10.7150/thno.42478 This issue Cite
Research Paper
SR9009 induces a REV-ERB dependent anti-small-cell lung cancer effect through inhibition of autophagy
1. Department of Oncology, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, 253 Industrial Avenue, Guangzhou, 510282, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510515, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
3. The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University, No.1023, South Shatai Road, Baiyun District, Guangzhou, 510515, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
4. Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510515, People's Republic of China.
5. Division of Laboratory Medicine, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, 253 Industrial Avenue, Guangzhou, 510282, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
6. Department of Research, Bioillus technology Co.Ltd, Guangzhou 510631, Guangdong, People's Republic of China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
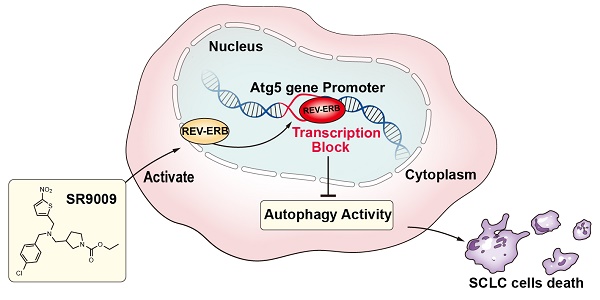
Rationale: The circadian clock coordinates cell proliferation and metabolism and impacts the progression of some diseases, particularly cancer. Pharmacological modulation of the circadian machinery may be an effective therapeutic approach for treating cancer. SR9009 is a specific synthetic agonist of the REV-ERBs, essential circadian clock components. However, the potential efficacy and antitumor mechanism of this drug in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) remains poorly understood.
Methods: Here, we used chemosensitive cells (H69 and H446) and the corresponding chemoresistant cells (H69AR and H446DDP) to assess the efficacy of the REV-ERB agonist SR9009 for the treatment of SCLC in vitro and further validated the antitumor effect in subcutaneous tumor models of SCLC. Then, we determined whether REV-ERBα was correlated with the anti-SCLC effect of SR9009. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) sequencing assays were conducted to identify potential DNA sequences directly regulated by REV-ERBα. Autophagy regulation by REV-ERBα and its possible mechanism in SR9009-based SCLC therapy were analyzed.
Results: Here, we showed that the REV-ERB agonist SR9009 is specifically lethal to both chemosensitive and chemoresistant SCLC cells. REV-ERBα was involved in the antitumor effect of SR9009 in SCLC. The core autophagy gene Atg5 was identified as a direct downstream target of REV-ERBα and was suppressed by the REV-ERB agonist SR9009 in SCLC. Furthermore, the interaction of REV-ERBα with this autophagy gene impaired autophagy activity, leading to SR9009 cytotoxicity in SCLC cells.
Principal conclusions: Our study provided a novel viewpoint indicating that the REV-ERB agonist SR9009 could be a novel and promising therapeutic strategy in first- or second-line SCLC treatment. The anti-SCLC effect of SR9009 is mediated by REV-ERB dependent suppression of autophagy via direct repression of the autophagy gene Atg5.
Keywords: small cell lung cancer, circadian clock component, SR9009, REV-ERB, autophagy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact