13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(4):1607-1620. doi:10.7150/thno.68232 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A multi-omics approach to identify molecular alterations in a mouse model of heart failure
1. Department of Cardiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University, Suzhou, China.
2. Thoracic Surgery Laboratory, The First College of Clinical Medicine, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China.
Abstract
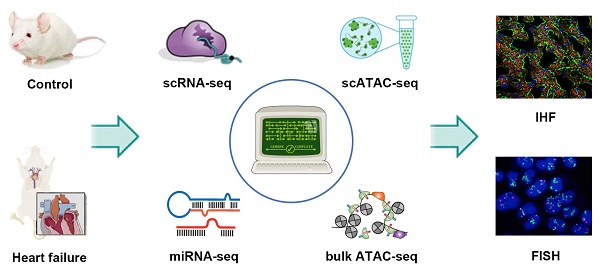
Rationale: The morbidity and mortality of heart failure (HF) have been increasing rapidly in recent years. However, the molecular events that link to the phenotype of HF remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the molecular alterations in the pathogenesis of HF induced by pressure overload.
Methods: Transverse aortic constriction was conducted to generate the HF mouse model. A multi-omics study was performed, including integrative analysis of scRNA-seq, scATAC-seq, bulk ATAC-seq and miRNA-seq data. The results of omics analysis were verified by immunofluorescence staining.
Results: scRNA-seq analysis identified five major cell types, which exhibits consistency with previous studies. Integrative analysis of ATAC-seq and miRNA-seq showed the alterations of gene expression in HF. Activation of genes involved in immune response at transcriptional level and perturbed expression of their upstream miRNAs confirmed the function of immune cells in the pathogenesis of HF. Analysis of scATAC-seq revealed a NO biosynthetic related gene regulation pattern in endothelial cells of failing hearts.
Conclusion: We performed a multi-omics analysis, comparing the transcriptomic, miRNA expression, and chromatin accessibility profile between the HF and control mice, thus providing mechanistic insights into the pathogenesis of pressure overload-induced HF.
Keywords: heart failure, multi-omics analysis, scRNA-seq, scATAC-seq
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact